Everyone once in their lifetime has undoubtedly encountered confirmation bias. Before I dive into the science-related part, let me present you with some real-life situations regarding this topic
When the elections are coming up, and you are a fervent supporter of a particular candidate, now, if the candidate does something through their campaign which probably was not beneficial to the common people, you choose to support it.
If your friend believes that a certain conspiracy theory is a truth they will seek the articles and resources which support their theory when they research the topic
When a particular skin care product does not work for a relative of yours, they are most likely to remember a negative image of it while forgetting or discounting the positive information when, in reality, it just might have been made for a different skin type.
All these examples are certain types of confirmation bias, which ill get into later on.
What is Confirmation Bias?
The examples do provide a general sense, but if I were to put it more simply, it would be the tendency for people to favour information that confirms their preconceived notions or beliefs. Perhaps you're thinking, "Is that not normal? It is normal for me to continue to support my favourite football club, right?" you could ask. Yes, it is normal, but in this case, ignoring facts and evidence makes you biased in favour of your opinions.
So… what is loyalty?
Although loyalty and confirmation bias appears to be extremely similar, there is a fine line of difference between them. In loyalty, there is an understanding that while we are open-minded and willing to hear different viewpoints, we nevertheless decide to defend our beliefs to some extent. If you truly believe that the cause you are backing is flawed, loyalty allows you to change. When we decide to fully dismiss evidence that contradicts our beliefs and support them irrationally, this turns into confirmation bias.
Types of Confirmation Bias
So at the start of the article I mentioned a couple of examples and how they are a certain type of confirmation bias, let me jump into that.
Selective interpretation bias - Here you tend to interpret the information the way it supports your belief, as mentioned in the first example.
Selective information bias - Also known as selective search bias, we can understand from the second example that we look for information which supports our existing theories and beliefs.
Selective memory bias - The third example, clearly shows that information confirming our beliefs are easier to remember than information which goes against it.
The most common source of Confirmation Bias
Something I should address and make everyone aware of is social media because it can undoubtedly cause confirmation bias. To keep you on their platform, social media will recommend content that supports the information you support, more often. Your exposure to opposing viewpoints is reduced, resulting in your beliefs appearing true to the letter.
While this is very controversial, religious faith can cause confirmation bias. What is your opinion, does it cause confirmation bias or not? Let me know.
How is this detrimental to our health?
At this point, it is pretty obvious how it is harmful to our critical thinking and the decisions we make, but to put it clearly, it can
Make individuals stubborn from changing their minds even when presented with overwhelming contradictory evidence to their beliefs
Prevent individuals from learning and growing
Make us live in deception or denial
The prevention mechanism
Well like most other mental health issues, firstly, we have to identify that we are living under confirmation bias. A way of doing this is actively seeking information which can contradict our beliefs. A few other tips are
Watching debates on the topic
Considering the opinions of people who are educated on the topic
Reading articles thoroughly before jumping to conclusions
Diving into the science and logic behind it
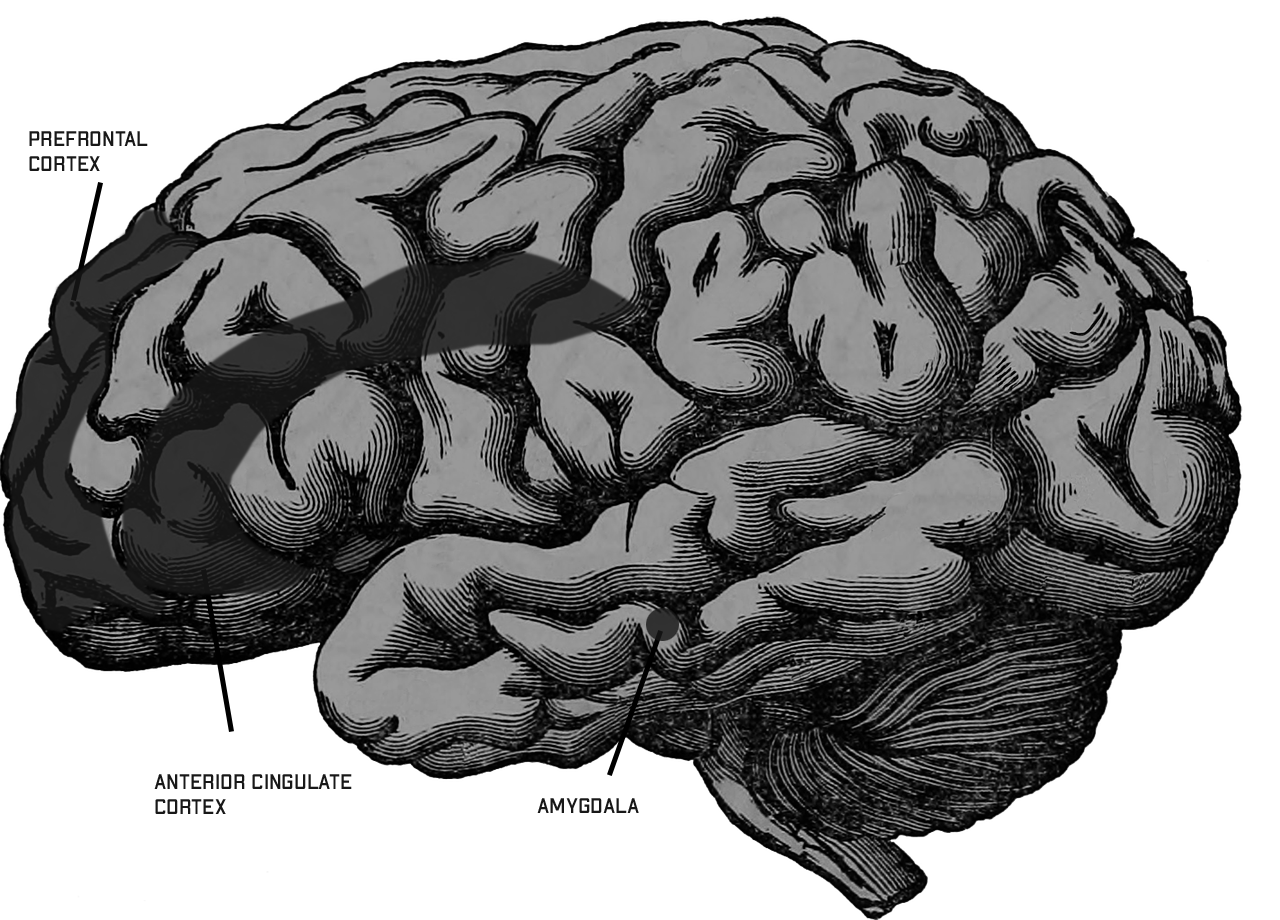
The Brain
If you want to delve a bit deeper, into which portions of the brain are responsible, this segment is for you.
Confirmation bias is influenced by several different regions, three of which are
Prefrontal Cortex - This portion is responsible for attention, memory and decision-making. If you have greater activation of this portion it shows that you are less likely to fall prey to confirmation bias and consider countervailing information.
Anterior Cingulate Cortex - In short, the ACC, is associated with monitoring the conflict between two pieces of information. The activation of this portion increases when you are presented with information which contradicts your beliefs
Amygdala - Decision-making and any emotional regulation require the amygdala of the brain. The amygdala is more active when you are presented with the material you believe in, indicating that the information is emotionally relevant, and less active, indicating that the piece of information is less salient.
Thanks!
Thank you for taking the time to read this article on Confirmation Bias. If you found it engaging and informative, please leave a like.
Have opinions on this topic? Please don’t forget to share them
If you have not already, you can subscribe below to receive these types of articles directly in your inbox as soon as they are published.